Introduction
In the realm of home solar energy storage, two prominent contenders vie for dominance: lead-acid batteries and lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries. Each type of battery comes with its own set of advantages and drawbacks, catering to different needs and preferences of homeowners seeking reliable energy storage solutions. In this comprehensive comparison, we will delve into the intricacies of both lead-acid and LiFePO4 batteries, exploring their design, performance, lifespan, maintenance requirements, and cost considerations.
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries have been a staple in energy storage applications for decades, offering a proven and cost-effective solution for homeowners looking to store surplus solar energy generated by their photovoltaic (PV) systems.
Design and Chemistry
Lead-acid batteries utilize a traditional lead-acid chemistry, which consists of lead plates submerged in a sulfuric acid electrolyte. These batteries are available in two main variants: flooded lead-acid batteries and valve-regulated lead-acid (VRLA) batteries. Flooded lead-acid batteries require regular maintenance, including topping up electrolyte levels, while VRLA batteries are maintenance-free and sealed.
Performance and Lifespan
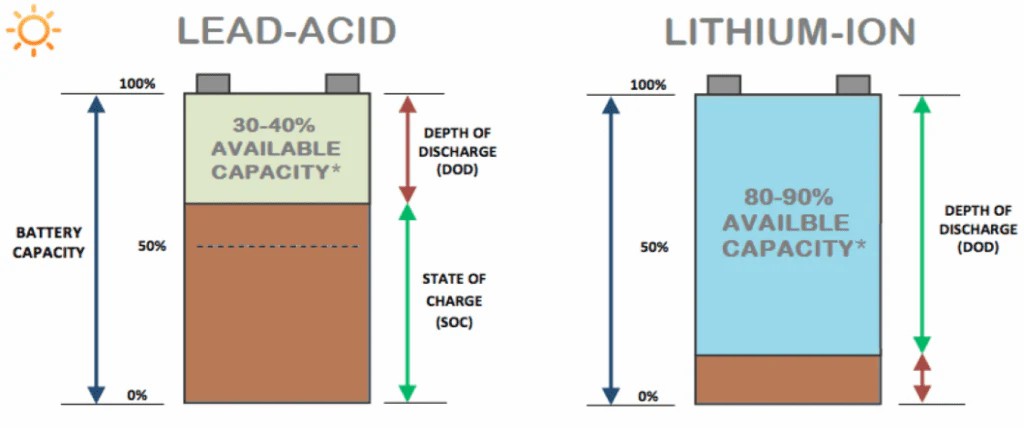
Lead-acid batteries are known for their durability and reliability, with a typical lifespan of 5 to 10 years depending on usage patterns and maintenance practices. However, they have relatively lower energy density and efficiency compared to LiFePO4 batteries, which may result in larger storage footprint requirements for achieving the desired energy storage capacity.
Maintenance and Safety
Flooded lead-acid batteries require periodic maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity, including checking electrolyte levels, cleaning terminals, and equalizing charges. VRLA batteries, on the other hand, offer maintenance-free operation but may be more susceptible to thermal runaway and overcharging if not properly monitored.
Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries have gained popularity in recent years due to their high energy density, efficiency, and longer lifespan compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
Design and Chemistry
LiFePO4 batteries utilize a lithium-ion chemistry with iron phosphate as the cathode material. This chemistry offers several advantages over lead-acid batteries, including higher energy density, faster charging rates, and improved cycle life.
Performance and Lifespan
LiFePO4 batteries boast a longer lifespan compared to lead-acid batteries, with some manufacturers claiming up to 10,000 cycles or more under optimal operating conditions. These batteries also exhibit higher energy efficiency, resulting in lower overall system losses and higher usable capacity.
Maintenance and Safety
LiFePO4 batteries require minimal maintenance compared to lead-acid batteries, with no need for electrolyte monitoring or equalization charges. However, proper charging and discharging protocols must be followed to prevent overcharging, overdischarging, and thermal runaway.
Comparison and Considerations
When choosing between lead-acid batteries and LiFePO4 batteries for home solar energy storage, several factors must be taken into consideration:
Energy Density
LiFePO4 batteries offer higher energy density compared to lead-acid batteries, allowing for smaller and more compact storage solutions.
Efficiency
LiFePO4 batteries are more energy-efficient than lead-acid batteries, resulting in lower overall system losses and higher usable capacity.
Lifespan
LiFePO4 batteries typically have a longer lifespan compared to lead-acid batteries, reducing the frequency and cost of battery replacements over time.
Cost Considerations
While LiFePO4 batteries may have a higher upfront cost compared to lead-acid batteries, their longer lifespan and higher efficiency may result in lower overall costs over the lifetime of the system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both lead-acid batteries and lithium iron phosphate batteries offer viable options for home solar energy storage, each with its own set of benefits and considerations. By carefully evaluating factors such as energy density, efficiency, lifespan, maintenance requirements, and cost considerations, homeowners can make informed decisions to select the best battery technology to meet their specific needs and goals for solar energy storage. Whether opting for the proven reliability of lead-acid batteries or the advanced performance of LiFePO4 batteries, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of reliable and sustainable energy storage solutions for years to come.
Post time: Apr-27-2024